Ingest quickstart
Get started creating an ingest pipeline
This guide will take you through the creation of an ingest pipeline.
Prerequisites
- Install RDI CLI.
- An existing Redis Enterprise cluster version >= 6.2.18
- RedisGears >= 1.2.6 installed on the cluster. In case it's missing, see Install RedisGears for Redis Data Integration to install.
- A target Redis database (can be added after installation).
Create a new RDI database
Run the create command to set up a new RDI database instance within an existing Redis Enterprise cluster:
redis-di create
The create command will create a BDB named redis-di-<ID> in your cluster. You will need to use a privileged Redis Enterprise user that has the permissions to create a BDB and to register RedisGears recipes.
Note: This command requires credentials of a Redis Enterprise cluster user with either
DB Member,Cluster Member, orCluster Adminroles. Seecluster roles for more information.
Scaffold configuration files
Review the scaffold command reference documentation before getting started with this step.
Run the scaffold command to generate configuration files for RDI and the Debezium Redis Sink Connector:
redis-di scaffold --db-type <cassandra|mysql|oracle|postgresql|sqlserver> --dir <PATH_TO_DIR>
The following files will be created in the provided directory:
├── debezium
│ └── application.properties
├── jobs
│ └── README.md
└── config.yaml
-
config.yamlis the RDI configuration file (definitions of target database, applier, and so on). -
debezium/application.propertiesis the Debezium Server configuration file. -
jobscontains information about your data transformation jobs. For more information, see data transformation pipeline.
Update Redis target connection details
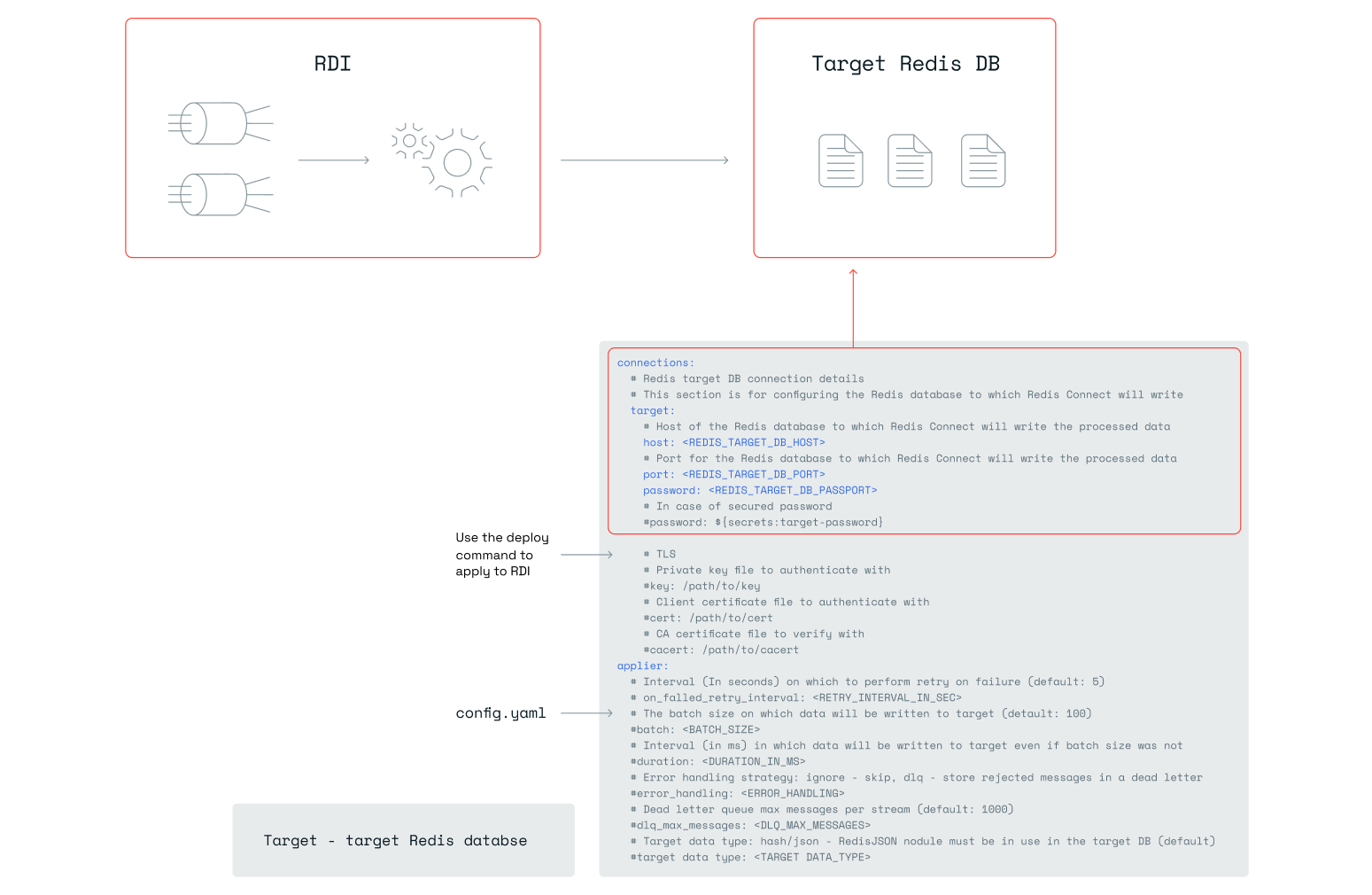
Edit the config.yaml configuration file. This file holds the connection details of the target Redis instance and applier settings.
Update the connection/target details to match the target database settings. See the configuration reference for all available settings.
Note: more than one Redis target can be defined in the configuration file and used later in RDI jobs to write data to different Redis databases at the same time.
Preventing data loss on the Redis target database
To prevent the Redis Target database from losing data, configure RDI to wait for replica shard write acknowledgment. This can be done by adding the following lines in the applier section of config.yaml:
applier:
wait_enabled: true
retry_on_replica_failure: true
Deploy the configuration
Run deploy command to deploy the local configuration to the remote RDI database:
redis-di deploy
Note: If you are specifying TLS
key,cert, andcacertlocations inconfig.yamlor you use one of the file patterns${file:<location>}or${file:<location>:<property-name>}for thepasswordproperty, make sure these files exist on the Redis Enterprise nodes that host RDI shards.
Validate the installation
Run redis-di status to check the status of the installation.
Note that it is okay to see the warning "No streams found" since we have not yet set up a Debezium source connector. We will do this in the next step.
Install the Debezium Server
Configure Debezium Server's application.properties
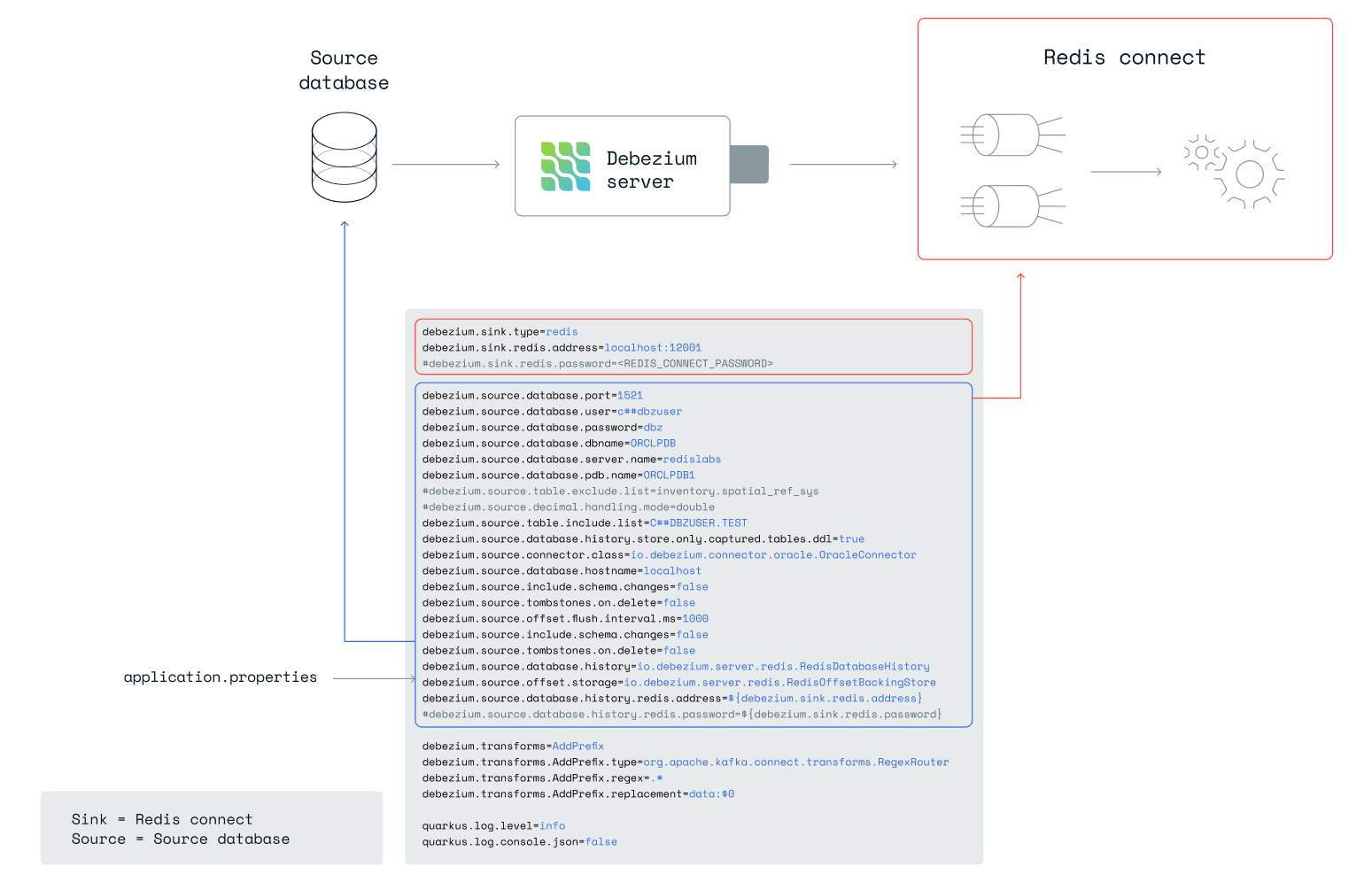
Edit the debezium/application.properties file in your project directory, which was created by the scaffold command described above.
See the Debezium Server configuration guide for the key configuration properties reference.
Run Debezium Server
Follow the Debezium Server deployment guide to deploy and run Debezium Server in either containerized or non-containerized deployment mode.
Quick database setup using Debezium example database
In case you want a quick setup of a preconfigured database to experiment with RDI, you can use one of the Debezium example databases.
To set up a Postgres example database:
docker run -it --name example-postgres -e POSTGRES_USER=postgres -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=postgres -p 5432:5432 debezium/example-postgres
RDI configuration file (config.yaml)
Reference guide
See RDI configuration file reference for detailed configuration file information.
Substitutions
-
${env:var}- environment variables. The environment variables will be prefixed withREDIS_DI_if not already prefixed that way. -
${file:<FILE_NAME>:<PROPERTY_NAME>}- specific property in the properties file. -
${file:<FILE_NAME>}- Reading the whole file. -
${secrets:secret_name}- secrets. To set the secret use theredis-di set-secretCLI command. The only supported secret is namedtarget-password.
Distributed installation
For information about a distributed installation (multi VM/Multi pod), see Distributed installation.
Installing from a Python package (whl file)
Note: RDI CLI requires Python version 3.7 or greater.
-
Set up a new virtual environment for Python:
python3.7 -m venv venv # replace with your version of Python -
Activate the virtual environment:
source venv/bin/activate -
Upgrade the pip command:
pip install --upgrade pip -
Install RDI CLI:
pip3 install https://qa-onprem.s3.amazonaws.com/redis-di/latest/redis_di_cli-latest-py3-none-any.whl
Upgrading
To learn how you can upgrade RDI CLI, RDI engine, and RedisGears see the Upgrade section.
Troubleshooting
See the troubleshooting guide.